tklog是rust高性能结构化日志库,支持同步日志,异步日志,支持自定义日志的输出格式,支持按时间,按文件大小分割日志文件,支持日志文件压缩备份,支持官方日志库标准API,支持mod独立参数设置
tklog相关信息
- 官网
- 项目源码
- 仓库
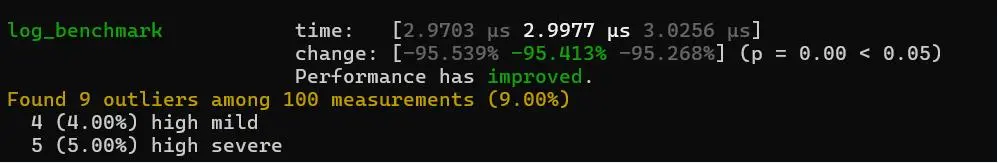
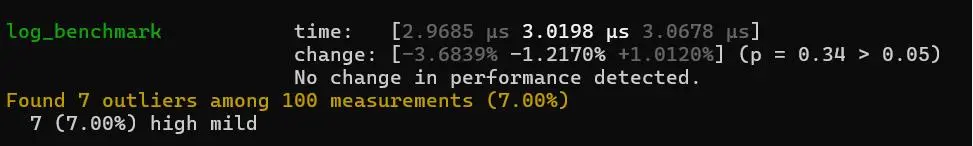
- 《tklog与log4rs 的基准测试》
tklog 0.0.8版本主要更新
1,优化代码并修复已知bug
2.支持模块设置独立日志参数
-
- tklog提供了
set_option与set_mod_option设置Logger对象的全局日志参数和指定mod的日志参数 - 在项目中,可以使用全局LOG对象,同时对多个mod设置独立的日志参数
- 不同mod可以设置不同的日志级别,日志格式,日志文件等
- 异步全局对象ASYNC_LOG的mod日志参数设置与同步LOG相同
- tklog提供了
说明:对指定的mod设置LogOption参数对象时,LogOption对象只作用于该mod。
在mod内部设置该mod的日志参数时,可以直接调用 module_path!() 来标识mod名,如:
tklog::LOG.set_mod_option(module_path!(),LogOption{level:Some(LEVEL::Info),console: Some(false),format:None,formatter:None,fileoption:None);
tklog 项目引入
[dependencies]
tklog = "0.0.8" # "0.0.x" 当前版本
set_option 示例:
tklog::LOG.set_option(LogOption{level:Some(LEVEL::Debug),console: Some(false),format:None,formatter:None,
fileoption: Some(Box::new(FileTimeMode::new("day.log",tklog::MODE::DAY,0,true)))});
LogOption对象说明
- level 日志级别
- format 日志格式
- formatter 日志输出自定义格式
- console 控制台日志设置
- fileoption 文件日志设置
set_mod_option 示例:
tklog::LOG.set_mod_option("testlog::module1",LogOption{level:Some(LEVEL::Debug),console: Some(false),format:None,formatter:None,
fileoption: Some(Box::new(FileTimeMode::new("day.log", tklog::MODE::DAY, 0,true)))});
testlog::module1为设置的模块名,可以通过rust内置宏module_path!()打印出当前模块名- 当tklog在模块
testlog::module1中使用时,将tklog将使用该LogOption对象
完整的设置mod参数 示例
mod module1 {
use std::{thread, time::Duration};
use tklog::{handle::FileTimeMode, LogOption, LEVEL};
pub fn testmod() {
tklog::LOG.set_mod_option(module_path!(), LogOption { level: Some(LEVEL::Debug), format: None, formatter: None, console: None, fileoption: Some(Box::new(FileTimeMode::new("module1.log", tklog::MODE::DAY, 0, true))) }).uselog();
tklog::debug!("module1,tklog api,LOG debug log>>", 123);
tklog::info!("module1,tklog api,LOG info log>>", 456);
log::debug!("module1,log api,debug log>>{}", 111);
log::info!("module1,log api,info log>>{}", 222);
thread::sleep(Duration::from_secs(1))
}
}
mod module2 {
use std::{thread, time::Duration};
use tklog::{handle::FileTimeMode, LogOption, LEVEL};
pub fn testmod() {
tklog::LOG.set_mod_option(module_path!(), LogOption { level: Some(LEVEL::Info), format: None, formatter: None, console: None, fileoption: Some(Box::new(FileTimeMode::new("module2.log", tklog::MODE::DAY, 0, true))) }).uselog();
tklog::debug!("module2,tklog api,LOG debug log>>", 123);
tklog::info!("module2,tklog api,LOG info log>>", 456);
log::debug!("module2,log api,debug log>>{}", 111);
log::info!("module2,log api,info log>>{}", 222);
thread::sleep(Duration::from_secs(1))
}
}
#[test]
fn testmod2() {
module1::testmod();
module2::testmod();
}
执行结果:
[DEBUG] 2024-06-19 10:54:07 testlog.rs 54:module1,tklog api,LOG debug log>>,123
[INFO] 2024-06-19 10:54:07 testlog.rs 55:module1,tklog api,LOG info log>>,456
[DEBUG] 2024-06-19 10:54:07 testlog.rs 56:module1,log api,debug log>>111
[INFO] 2024-06-19 10:54:07 testlog.rs 57:module1,log api,info log>>222
[INFO] 2024-06-19 10:54:08 testlog.rs 68:module2,tklog api,LOG info log>>,456
[INFO] 2024-06-19 10:54:08 testlog.rs 70:module2,log api,info log>>222
示例2: 异步日志
mod module3 {
use tklog::{handle::FileTimeMode, Format, LogOption, LEVEL};
pub async fn testmod() {
tklog::ASYNC_LOG.set_mod_option("testlog::module3", LogOption { level: Some(LEVEL::Debug), format: Some(Format::Date), formatter: None, console: None, fileoption: Some(Box::new(FileTimeMode::new("module3.log", tklog::MODE::DAY, 0, true))) }).await.uselog();
tklog::async_debug!("async module3,tklog api,LOG debug log>>", 123);
tklog::async_info!("async module3,tklog api,LOG info log>>", 456);
log::debug!("async module3,log api,debug log>>{}", 333);
log::info!("async module3,log api,info log>>{}", 444);
tokio::time::sleep(tokio::time::Duration::from_secs(1)).await;
}
}
mod module4 {
use tklog::{handle::FileTimeMode, Format, LogOption, LEVEL};
pub async fn testmod() {
tklog::ASYNC_LOG.set_mod_option("testlog::module4", LogOption { level: Some(LEVEL::Info), format: Some(Format::Date), formatter: None, console: None, fileoption: Some(Box::new(FileTimeMode::new("module4.log", tklog::MODE::DAY, 0, true))) }).await.uselog();
tklog::async_debug!("async module4,tklog api,LOG debug log>>", 123);
tklog::async_info!("async module4,tklog api,LOG info log>>", 456);
log::debug!("async module4,log api,debug log>>{}", 333);
log::info!("async module4,log api,info log>>{}", 444);
tokio::time::sleep(tokio::time::Duration::from_secs(1)).await;
}
}
#[tokio::test]
async fn testmod4() {
module3::testmod().await;
module4::testmod().await;
}
执行结果:
[DEBUG] 2024-06-19 10:59:26 testlog.rs 85:async module3,tklog api,LOG debug log>>,123
[INFO] 2024-06-19 10:59:26 testlog.rs 86:async module3,tklog api,LOG info log>>,456
[DEBUG] 2024-06-19 10:59:26 testlog.rs 87:async module3,log api,debug log>>333
[INFO] 2024-06-19 10:59:26 testlog.rs 88:async module3,log api,info log>>444
[INFO] 2024-06-19 10:59:27 testlog.rs 98:async module4,tklog api,LOG info log>>,456
[INFO] 2024-06-19 10:59:27 testlog.rs 100:async module4,log api,info log>>444
说明,上述示例上
- module1 ,module2 的mod名调用
module_path!()设置,module3 ,module4则显示写明testlog::module3,testlog::module4 ,可以看到效果是一样的。 - 模块设置的参数如果未None时,则会使用全局的参数。如
tklog::LOG
.set_option(LogOption{level:Some(LEVEL::Debug),console: Some(false),format:None,formatter:None,fileoption: Some(Box::new(FileTimeMode::new("day.log",tklog::MODE::DAY,0,true)))})
.set_mod_option("testlog::module", LogOption { level: Some(LEVEL::Inof), format: None, formatter: None, console: None, fileoption: None });
-
- 对模块 testlog::module 只设置了 level,其他的参数则会直接使用全局参数,如 fileoption,默认为 FileTimeMode::new("day.log",tklog::MODE::DAY,0,true)
版本性能基准测试